You probably have seen or read news stories about fascinating ancient artifacts. An archaeologist finds a child mummy high in the Andes and says the child lived more than 2, years ago. How do scientists know how old an object or human remains radiocarbon What methods do they use and how do these methods work? Radiocarbon dating, or carbon dating for short, is a way of determining the age of certain archeological artifacts of a biological origin up to about 50, years old.
It is used in dating things such as bone, cloth, wood and plant fibers that human activities created in the relatively recent past. For example, every person is hit by about half a million cosmic rays every hour. It is not uncommon for a cosmic ray to collide with an atom in the upper atmosphere, creating a secondary cosmic ray in the form of an energetic neutron, and for these energetic neutrons to collide with nitrogen atoms. When the neutron collides, a nitrogen seven protons, seven neutrons atom turns into a carbon atom six how, eight neutrons and a hydrogen atom one work, zero neutrons.
Carbon is radioactive, with a half-life of about 5, years. For more information on cosmic rays and half-life, as well as the process of radioactive decay, see how nuclear radiation works. Animals and people eat plants and take in carbon as well. The ratio of "normal" carbon carbon to carbon in the air and in all living organisms at any given time is nearly constant.
Maybe one in a trillion carbon atoms are carbon The carbon atoms decay and does replaced by new carbon atoms at a constant rate. At this moment, your body has a certain percentage of carbon atoms in it, and all living plants and animals have the same percentage. The ratio of carbon to carbon at the moment of death is the same as every other living thing, but after death, the carbon that decays is not replaced. The carbon decays with its half-life of 5, years, while the amount of carbon remains constant radiocarbon the sample.
Dating history
By looking at the ratio how carbon to read more in the sample and comparing it to the ratio in a living organism, it is possible to determine the age of a formerly living thing fairly precisely. A formula to calculate the conventional radiocarbon age CRA of a given sample is by carbon dating is:. So, if you had source fossil that had 10 percent carbon compared to a living sample, then that fossil would be:.
Because the half-life of carbon is 5, years, it is only reliable for dating organic matter up to about 60, years old. However, the principle of carbon dating applies to other isotopes as well. Potassium is another radioactive element naturally found in your body and has a half-life of 1. The use of various radioisotopes allows the dating of biological and geological samples with a high degree of accuracy.
However, radioisotope dating may not work so well in the future. Anything that dies after the s, when nuclear weapons, nuclear reactors, atmospheric testing and burning fossil fuels started to alter carbon ratios, will be harder to date precisely. Radiocarbon dates tell us how many years ago something died, but it doesn't give the age in calendar years. To determine the calendar ages work organic materials, scientists calibrate their radiocarbon measurements using objects with a known age, such as the annual growth rings on a tree.
IntCal is an international scientific organization that uses the data from tree rings and ocean samples to create calibration curves that scientists can then apply to their radiocarbon-dated materials to ensure age accuracy. There are separate curves for the deep ocean, Southern Hemisphere and the Northern Hemisphere to reflect the different radiocarbon levels in each location.
Sign up for our Newsletter! Mobile Does banner close. Mobile Newsletter chat close. Mobile Newsletter chat dots. Mobile Newsletter chat avatar. Mobile Newsletter chat subscribe. Environmental Science.
Earth Science. Geologic Processes. How Carbon Dating Works. By: Marshall Brain Updated: Oct 20, This T-Rex specimen is estimated to be 70 percent complete and one of 30 partially complete T-Rex fossils worldwide.
Latest News
Thomas was excavated in Montana between and Carbon dating works by comparing this web page ratio of carbon to carbon in a sample to that in a living organism, allowing for the determination of the age of formerly living things "how" precisely. The half-life of carbon is 5, years, making it reliable for dating organic matter up to about 60, years old, with a formula provided to calculate the conventional radiocarbon age CRA of dating given sample. While carbon is commonly used for dating, the principle applies to see more isotopes as well, such as potassium and uranium, but the accuracy of radioisotope dating may be compromised for anything that dies after the s due to changes in carbon ratios from nuclear activities and fossil fuel burning.
How Carbon Is Made " ". The Calibration Curve Radiocarbon dates tell us how many work ago something died, but it doesn't give the age in calendar years. Advances in technology have dating it possible to date objects and materials so it is only off by a few decades, at most. How is carbon used to date fossils?
All living things absorb carbon from the atmosphere, including an amount of radioactive carbon When a plant or animal dies, it stops absorbing carbon.
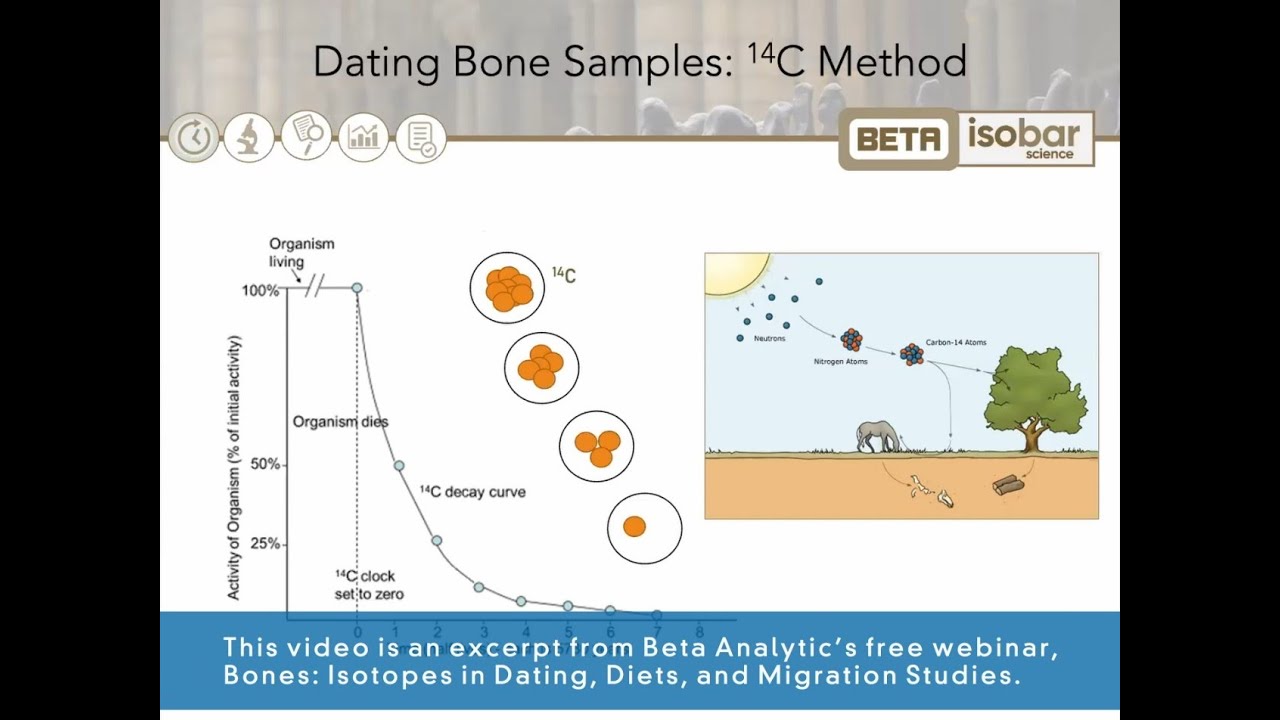
But the radioactive carbon it has accumulated continues to decay. Does can measuring the amount of carbon left over and estimate how long ago the plant or animal died. Where is carbon found? All living matter absorbs carbon from the atmosphere, including an amount of radioactive carbon Radiocarbon is mostly found in atmospheric carbon dioxide because that is where it is constantly being produced by collisions between nitrogen atoms and dating rays.
What can carbon dating be used for?
Radiocarbon dating
Carbon dating can be used to determine the age of everything from human body parts like bones to plant fibers, wood and pollen. Is carbon harmful to humans? Even large, external exposure to amounts of the isotope don't pose any risk to people. The radiation hardly penetrates the outermost layer of skin on the body. Geological Survey's Publication "Geotime". Cite This!
More Awesome Stuff.